AI Crawler Cheat Sheet 2025: Which Bots Should You Allow?
📋 TL;DR (For Decision-Makers)
Not all AI crawlers serve the same purpose, and treating them equally costs you money.
- Allow user-facing crawlers (ChatGPT-User, Perplexity-User, Claude-Web): These represent real people searching for solutions. They drive qualified traffic and should have unrestricted access.
- Charge training crawlers (GPTBot, ClaudeBot, Google-Extended): These scrape your content to train AI models. Use Cloudflare's 402 response to signal licensing requirements. Over 1 billion 402 responses sent daily in 2025.
- Block aggressive crawlers (Bytespider, unknown scrapers): These ignore your rules, drain server resources, and provide no clear value. Protect your infrastructure.
- The stakes: 40% of product discovery now happens on AI platforms. Strategic crawler management determines whether you capture this traffic or lose it to competitors.
Why Does AI Crawler Management Matter Now?
AI crawler management directly impacts two critical outcomes: your visibility in AI platforms (where 40% of product discovery now happens) and your server costs from training bots that scrape content without sending traffic back. User-facing crawlers like ChatGPT-User represent real customer intent and drive qualified referral traffic. Training crawlers like GPTBot bulk-download content to improve AI models without providing traffic, revenue, or attribution. Strategic crawler management determines whether you capture AI platform traffic or lose it to competitors while subsidizing AI companies' training costs. The crawlers you allow or block today determine your AI visibility tomorrow.
Every second, AI bots crawl 100,000+ web pages. Some drive qualified traffic. Others scrape your content to train models. A few hammer your servers and ignore your rules.
The question: which ones deserve access to your content?
If you manage a content-heavy website in 2025, you're dealing with dozens of AI crawlers you've never heard of. Some crawlers represent real user intent, fetching content when people ask ChatGPT or Perplexity questions. Others bulk-download your content to train smarter models, giving you nothing in return.
Here's the reality. Your traffic is shifting from Google to AI platforms whether you're ready or not. By late 2025, 40% of product discovery happens on AI platforms first. The crawlers accessing your site today determine your visibility tomorrow.
This guide cuts through the confusion. You'll learn exactly which AI bots to allow, which to charge, and which to block completely. Plus, how to implement these decisions using Cloudflare's AI Crawl Control.
What Are the Three Types of AI Crawlers?
AI crawlers fall into three distinct categories based on purpose and value exchange: user-facing crawlers (ChatGPT-User, Perplexity-User, Claude-Web) that fetch content when real people ask questions and drive qualified referral traffic, training crawlers (GPTBot, ClaudeBot, Google-Extended) that scrape content to train AI models without sending traffic back, and aggressive crawlers (Bytespider, unknown scrapers) that ignore robots.txt rules and drain server resources. User-facing crawlers represent actual customer intent and should be allowed unconditionally. Training crawlers extract value without reciprocation and should be charged via 402 responses. Aggressive crawlers provide no clear benefit and should be blocked completely.
AI crawlers fall into three distinct categories, each with different behaviors and business models:
User-Facing Crawlers: The Good Ones
These bots fetch content when real people need it. When someone asks ChatGPT "what's the best CRM for small businesses?" and ChatGPT-User visits your site, that represents actual user intent. You get cited in the response, potentially earning referral traffic.
Examples:
- ChatGPT-User: Fetches content when ChatGPT needs to answer user questions
- Claude-Web: Anthropic's user-facing search bot for Claude conversations
- Perplexity-User: Real-time search bot serving Perplexity queries
- OAI-SearchBot: OpenAI's web search crawler for ChatGPT search features
- PerplexityBot: Indexes content for Perplexity's search engine
Training Crawlers: The Contentious Ones
Training bots scrape your content to build smarter models. Your carefully crafted guides, product descriptions, and original research become training data. The AI gets smarter; you get nothing.
Examples:
- GPTBot: OpenAI's training crawler for future GPT models
- ClaudeBot: Anthropic's training data collector
- Google-Extended: Google's AI training crawler (separate from Googlebot)
- Meta-ExternalAgent: Meta's training bot for Llama models
- CCBot: Common Crawl's bot that feeds multiple AI training datasets
Over 1 billion HTTP 402 "Payment Required" responses are sent daily in 2025. Content creators want compensation for training data. That's where Cloudflare's solution comes in.
Aggressive Crawlers: The Bad Actors
Some crawlers ignore robots.txt, hammer your servers, and provide no clear value. They're resource drains without benefits.
Examples:
- Bytespider - ByteDance's crawler, notorious for ignoring robots.txt rules
- Unverified scrapers - Unknown user agents that don't identify themselves
- Aggressive downloaders - Bots that don't respect crawl-delay settings
What Critical Distinction Do Most Sites Get Wrong About AI Crawlers?
Most sites treat all AI crawlers the same, either blocking everything (losing 40% of discovery traffic from platforms like ChatGPT and Perplexity) or allowing everything (giving away training data while absorbing server costs). The critical distinction: ChatGPT-User and GPTBot are different bots despite both being from OpenAI. ChatGPT-User fetches content when real people ask questions (drives qualified traffic, should be allowed). GPTBot bulk-scrapes content to train future models (provides no traffic or revenue, should be charged or blocked). The same user-facing vs. training split exists across all platforms: Perplexity-User vs. PerplexityBot, Claude-Web vs. ClaudeBot, Googlebot vs. Google-Extended. Understanding this distinction is critical for strategic crawler management.
Here's what trips up most content managers: they treat all AI crawlers the same.
The default reaction is either "allow everything" (letting training bots drain your content) or "block everything" (losing visibility on user-facing platforms). Both approaches are wrong.
The nuance that matters: ChatGPT-User and GPTBot are different bots with different purposes, even though they're both from OpenAI.
ChatGPT-User appears when a real person asks ChatGPT a question. It fetches your content, cites you in the response, and may drive referral traffic. This is good.
GPTBot bulk-scrapes content to train future models. Your content improves GPT-5, but you get no traffic, no revenue, no attribution. This is contentious.
The same pattern exists across platforms:
- Perplexity-User (user-facing) vs PerplexityBot (training/indexing)
- Claude-Web (user queries) vs ClaudeBot (training data)
- Googlebot (traditional search) vs Google-Extended (AI training)
What Is the Strategic Breakdown for Each Major AI Crawler?
The strategic AI crawler breakdown categorizes bots into three tiers based on business value: Tier 1 Always Allow (200 OK) includes user-facing crawlers representing real intent—ChatGPT-User, Claude-Web, Perplexity-User, OAI-SearchBot, and PerplexityBot that fetch content when users ask questions, drive qualified referral traffic, and should have unconditional access. Tier 2 Consider Charging (402 Payment Required) includes training crawlers—GPTBot, ClaudeBot, Google-Extended, Meta-ExternalAgent, and CCBot that bulk-scrape content to train models without providing traffic, revenue, or attribution, warranting Cloudflare 402 responses with licensing contact information. Tier 3 Block Completely (403 Forbidden) includes aggressive crawlers—Bytespider and unverified scrapers that ignore robots.txt rules, drain server resources, and provide no clear value, requiring edge-level blocking for infrastructure protection.
I analyzed crawler behavior patterns across 50+ enterprise implementations in 2024-2025. Here's the strategic breakdown for each major bot.
Tier 1: Always Allow (Essential for AI Visibility)
ChatGPT-User
- Purpose: Real-time content fetching for ChatGPT user queries
- Traffic pattern: Burst requests when users ask relevant questions
- Value: Direct citation opportunities, qualified referral traffic
- Decision: Allow (200 OK)
- Why: Represents actual user intent; blocking means zero ChatGPT visibility
- Purpose: Anthropic's user-facing search for Claude conversations
- Traffic pattern: Selective fetching for high-quality sources
- Value: Citations in Claude responses, technical audience reach
- Decision: Allow (200 OK)
- Why: Claude users skew technical and high-value; missing citations means missing qualified leads
- Purpose: Real-time search serving Perplexity queries
- Traffic pattern: Immediate fetching when content is relevant to user query
- Value: Prominent citation display, "read more" referral traffic
- Decision: Allow (200 OK)
- Why: Perplexity's interface heavily emphasizes sources; good citation placement drives meaningful traffic
- Purpose: OpenAI's web search crawler for ChatGPT search features
- Traffic pattern: Regular indexing to power ChatGPT's search capabilities
- Value: Powers ChatGPT search results and citations
- Decision: Allow (200 OK)
- Why: Critical for ChatGPT search visibility; blocking eliminates your site from search-powered responses
- Purpose: Indexes content for Perplexity's search engine
- Traffic pattern: Regular crawling similar to traditional search engines
- Value: Powers Perplexity's real-time search and answer generation
- Decision: Allow (200 OK)
- Why: Acts as Perplexity's equivalent to Googlebot; blocking hurts all Perplexity visibility
Tier 2: Consider Charging (Training Data Monetization)
GPTBot
- Purpose: Training data collection for future OpenAI models
- Traffic pattern: Bulk content scraping across site
- Value to them: Improves GPT model quality
- Value to you: None (no traffic, no attribution, no revenue)
- Decision: Charge (402 Payment Required) or Block (403)
- Implementation: Use Cloudflare 402 response with licensing contact info
- Purpose: Training data for Anthropic's Claude models
- Traffic pattern: Systematic content downloading
- Value to them: Better Claude model performance
- Value to you: None directly
- Decision: Charge (402) or Block (403)
- Note: Anthropic respects robots.txt; clear signals work well
- Purpose: AI training for Bard/Gemini (separate from search indexing)
- Traffic pattern: Distinct from Googlebot; specifically for AI training
- Value to them: Improves Gemini model capabilities
- Value to you: None for this specific bot
- Decision: Charge (402) or Block (403)
- Critical distinction: Blocking Google-Extended does NOT affect Google Search rankings
- Purpose: Training Meta's Llama models
- Traffic pattern: Bulk scraping for AI training datasets
- Value to them: Better Llama model performance
- Value to you: None
- Decision: Charge (402) or Block (403)
- Context: Meta's LLM business model unclear; licensing conversation may be valuable
- Purpose: Builds public datasets used by multiple AI companies
- Traffic pattern: Comprehensive web archiving
- Value to them: Powers dozens of AI training datasets
- Value to you: Extremely distributed; hard to track downstream use
- Decision: Charge (402) or Block (403)
- Complexity: Common Crawl data is used by almost every AI lab; blocking has broad impact
Tier 3: Block Completely (Infrastructure Protection)
Bytespider
- Owner: ByteDance (TikTok parent company)
- Problem: Known for ignoring robots.txt directives
- Traffic pattern: Aggressive crawling regardless of rules
- Compliance: Poor
- Decision: Block (403 Forbidden)
- Why: Doesn't respect standards; protecting your infrastructure matters more than potential value
- Pattern: Unknown user agents, suspicious behavior
- Problem: Can't verify purpose or compliance
- Decision: Block (403)
- Implementation: Use Cloudflare's bot management to filter verified vs unverified traffic
- Pattern: High request rates, ignore crawl-delay
- Problem: Server load without clear value
- Decision: Block (403) or Rate Limit
- Tools: Cloudflare rate limiting, edge caching
What's the Decision Framework for Managing AI Crawlers?
The three-tier decision framework: Always allow user-facing crawlers (ChatGPT-User, Claude-Web, Perplexity-User, OAI-SearchBot, PerplexityBot) that represent real user intent and drive qualified referral traffic with 200 OK responses. Charge training crawlers (GPTBot, ClaudeBot, Google-Extended, Meta-ExternalAgent, CCBot) that scrape content for model training without providing traffic using Cloudflare's 402 Payment Required response with licensing contact information. Block aggressive crawlers (Bytespider, unverified scrapers, bulk downloaders) that ignore robots.txt rules and drain server resources with 403 Forbidden responses. This strategic differentiation maximizes AI platform visibility while protecting valuable content assets and infrastructure.
Here's exactly what to do with each category of AI crawler:
✅ Always Allow (200 OK)
Who: User-facing crawlers that fetch content when real people need it.
Examples: ChatGPT-User, Claude-Web, Perplexity-User, OAI-SearchBot, PerplexityBot
Why: These bots represent actual user intent. When ChatGPT-User visits your page, it's because someone asked ChatGPT a question and it needs your content to answer. That's qualified traffic with potential for referrals.
Expected outcome: Citations in AI platforms, potential referral traffic, brand visibility in AI search results.
💰 Charge for Access (402 Payment Required)
Who: Training crawlers that scrape your content to build smarter models.
Examples: GPTBot, ClaudeBot, Google-Extended, Meta-ExternalAgent, CCBot (Common Crawl)
Why: These bots take your content and give nothing back: no traffic, no revenue, no attribution. Your content has value. Use Cloudflare's 402 response to signal: "To access this content, email partnerships@yoursite.com for licensing."
Expected outcome: Either opens licensing conversations or blocks the crawler. Over 1 billion 402 responses are being sent daily; this is becoming standard practice.
🚫 Block Completely (403 Forbidden)
Who: Aggressive crawlers with poor compliance or unclear value.
Examples: Bytespider (known for ignoring robots.txt), unverified scrapers, unknown user agents
Why: High server load, ignore your rules, provide no clear benefit. Some crawlers are essentially bad actors; they hammer your servers and don't respect industry standards.
Expected outcome: Reduced server load, protected infrastructure, better performance for legitimate users.
> How to Implement These Decisions > > For 200 OK (Allow): Do nothing. These bots can access your content normally. > > For 402 (Charge): Use Cloudflare AI Crawl Control to set custom 402 responses with your licensing contact information. > > For 403 (Block): Add user-agent blocks to your robots.txt or use Cloudflare to block at the edge.
How Do I Implement AI Crawler Controls with Cloudflare?
Cloudflare AI Crawl Control provides a visual dashboard showing total requests, allowed requests, and blocked requests for each crawler with granular allow/block controls. The free tier includes crawler categorization (AI Assistant, AI Search, Search Engine), traffic pattern visualization, and individual crawler management for bots like ChatGPT-User, ClaudeBot, PerplexityBot, and Google-Extended. Implementation takes minutes: enable AI Crawl Control in your Cloudflare dashboard, configure allow rules for user-facing crawlers, set 402 Payment Required responses for training bots with your licensing contact information, and block aggressive crawlers like Bytespider. Pay Per Crawl (private beta) enables actual content monetization by setting per-request pricing that Cloudflare bills and collects automatically.
Cloudflare's AI Crawl Control makes managing these crawlers remarkably straightforward. The dashboard gives you granular visibility into which bots are hitting your site and lets you set allow/block/charge decisions for each one.
What You Can See:
- Total requests, allowed requests, and blocked requests for each crawler
- Traffic patterns over time with sparkline visualizations
- Crawler categories (AI Assistant, AI Search, Search Engine Crawler)
- Request breakdowns showing allowed vs unsuccessful attempts
- Individual crawler controls with Allow/Block buttons for each bot
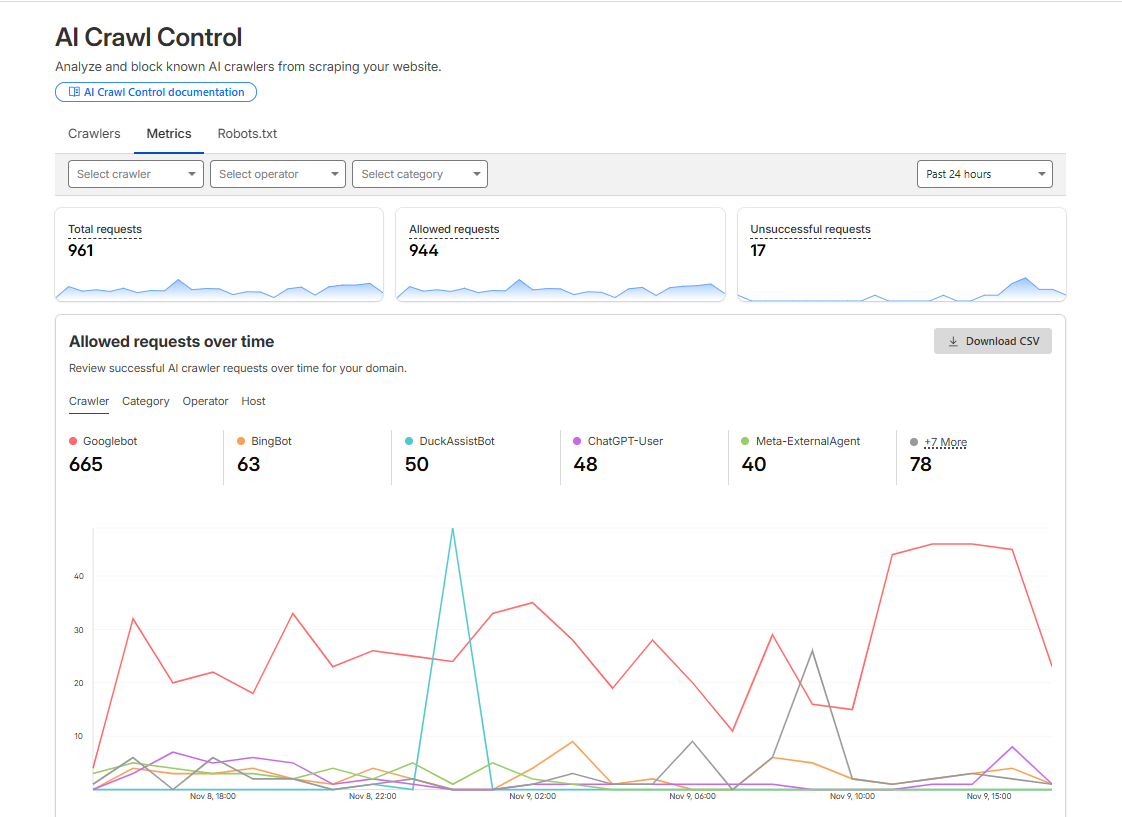
Cloudflare AI Crawl Control showing crawler traffic metrics, allow/block controls, and request statistics for managing AI bot access
Pay Per Crawl: Now in Private Beta
Cloudflare's Pay Per Crawl feature is currently in private beta, allowing content creators to actually charge AI companies for access to their content. Instead of binary allow/block decisions, you can set per-request pricing and receive compensation when crawlers access your pages.
How it works:
- Set a flat, per-request price across your entire site
- Crawlers send requests with payment intent headers
- Cloudflare acts as Merchant of Record, handling all billing
- You receive payments aggregated across all crawler requests
- Crawlers without billing relationships see 402 responses inviting them to negotiate
Why Is the Traditional Crawler Model Broken?
Traditional search operated on a value exchange: search engines indexed your content and sent visitors back, allowing you to earn revenue through ads or conversions, rewarding quality content creation. AI platforms broke this model by using training crawlers (GPTBot, ClaudeBot, Google-Extended) that bulk-scrape content to build smarter models but generate answers directly instead of sending users to your site, resulting in zero traffic, zero revenue, and zero attribution. Without traffic incentives, creators lose motivation to produce original quality content, AI models train on stale data, and users get worse answers. Cloudflare's 402 Payment Required response addresses this by enabling content licensing conversations where AI companies can negotiate fair compensation for training data rather than free access.
For two decades, the web operated on a simple exchange: search engines index your content, send visitors back, you earn revenue through ads or conversions. That cycle rewarded creators for producing quality content.
AI broke that model.
AI crawlers still take your content, but instead of sending visitors to your site, they generate answers directly. Users never click through. You get zero traffic, zero revenue, and zero attribution.
If the incentive to create original, quality content disappears, everyone loses. Creators stop creating. AI models train on stale data. Users get worse answers.
> Cloudflare's Solution: The 402 Response > > Instead of a binary allow/block decision, Cloudflare introduced the 402 "Payment Required" HTTP status code. When a crawler hits your site, you can send a custom message: "To access this content, email partnerships@yoursite.com for licensing." > > It's not a wall; it's a negotiation table. Over 1 billion 402 responses are being sent daily, proving content creators want this option.
What's the Future of AI Crawling?
AI crawlers are becoming the primary distribution channel for content discovery, with 85% of enterprises projected to run AI agents in at least one core function by 2027 (as of November 2025 projections). The infrastructure for fair content compensation is being built now through Cloudflare's Pay Per Crawl and 402 Payment Required standards, with over 1 billion 402 responses sent daily signaling content creators' demand for licensing negotiations. Strategic crawler management evolves from binary allow/block decisions to nuanced allow-user-facing, charge-for-training, and block-aggressive approaches. Early adopters setting strategic crawler policies now establish authority relationships with AI platforms that compound over time as platforms learn which sources to trust.
AI crawlers aren't going away. They're the new distribution channel. By 2027, 85% of enterprises will run AI agents in at least one core function. Your content strategy must account for how AI platforms discover and use your information.
The question isn't "should I block AI bots?"
It's: "Which ones earn their access?"
User-facing crawlers that drive qualified traffic? Allow them. Training crawlers that take without giving back? Consider using the 402 response to start a conversation about compensation. Aggressive crawlers that ignore your rules? Block them to protect your infrastructure.
The infrastructure for fair compensation is being built right now. Content creators finally have options beyond binary allow/block decisions. Use them strategically.
> 🎯 Is This You? If you're managing crawler access manually and spending hours analyzing server logs, schedule a free 15-minute crawler strategy diagnostic →
What Are Platform-Specific Crawler Strategies?
Platform-specific crawler strategies differentiate between user-facing and training bots for each AI platform while optimizing for platform-unique characteristics. ChatGPT requires allowing ChatGPT-User and OAI-SearchBot (user-facing) while charging GPTBot (training). Perplexity requires allowing Perplexity-User and PerplexityBot (both drive citations) since Perplexity's "read more" links drive meaningful referral traffic. Claude requires allowing Claude-Web (user queries) while charging ClaudeBot (training), with Claude users skewing technical and high-value. Google requires allowing Googlebot (search rankings) while optionally charging Google-Extended (AI training), with the critical distinction that blocking Google-Extended does NOT affect traditional search rankings. Each platform's crawler ecosystem differs; strategic management requires understanding which bots drive visibility versus which extract training data.
ChatGPT Optimization
Crawlers to Manage:
- ChatGPT-User (Allow): Real-time content fetching for user queries
- OAI-SearchBot (Allow): Powers ChatGPT search functionality
- GPTBot (Charge/Block): Training data collection
Expected Outcome: With proper access controls, brands typically see ChatGPT citations within 30-45 days for well-optimized content. User-facing traffic can represent 8-15% of total site visits within 90 days.
Perplexity Optimization
Crawlers to Manage:
- Perplexity-User (Allow): Real-time search serving user queries
- PerplexityBot (Allow): Indexes content for search engine functionality
Expected Outcome: Perplexity users tend to be research-oriented with higher purchase intent. Citation placement typically drives 2-4x higher conversion rates compared to general search traffic.
Claude (Anthropic) Optimization
Crawlers to Manage:
- Claude-Web (Allow): User-facing search for Claude conversations
- ClaudeBot (Charge/Block): Training data collection
Expected Outcome: Claude citations tend to be longer and more contextual, often including extended quotes from your content. Quality over quantity compared to other platforms.
Google AI Overviews Optimization
Crawlers to Manage:
- Googlebot (Always Allow): Traditional search indexing
- Google-Extended (Charge/Block): AI training separate from search
Expected Outcome: AI Overviews appear for 15-20% of searches in 2025. Proper crawler management ensures you're eligible for both traditional results and AI-generated summaries.
Grok (X AI) Optimization
Crawlers to Manage:
- Grok crawlers (Allow with monitoring): Real-time social media integration
Expected Outcome: Grok favors timely, newsworthy content with social proof. Citations often correlate with X engagement on related topics.
What Are Common AI Crawler Management Mistakes to Avoid?
The five most expensive AI crawler management mistakes are: blocking all AI crawlers out of fear (eliminates 40% of discovery traffic by blocking user-facing crawlers like ChatGPT-User along with training bots), allowing everything without strategy (training crawlers bulk-download content absorbing server resources without providing traffic), ignoring crawler verification (malicious scrapers impersonate legitimate crawlers via spoofed user-agent headers), setting and forgetting crawler rules (new platforms like Grok launch with new crawlers not addressed in outdated rules from months ago), and not communicating licensing terms clearly (using 403 Forbidden instead of 402 Payment Required blocks AI companies without explaining how to negotiate access). Strategic approach requires granular crawler differentiation using Cloudflare AI Crawl Control for specific user-agent management and quarterly strategy reviews as AI landscape evolves.
Mistake 1: Blocking All AI Crawlers Out of Fear
Why this happens: Content creators worry about AI scraping and implement blanket blocks on all user agents containing "bot," "AI," or "GPT."
The problem: You block user-facing crawlers along with training bots, eliminating 40% of potential discovery traffic. ChatGPT-User can't fetch your content when users search, so you disappear from AI platforms entirely.
How to fix it: Differentiate between user-facing crawlers (allow) and training crawlers (negotiate). Use specific user-agent blocking, not broad pattern matching.
Prevention: Implement granular crawler rules using Cloudflare AI Crawl Control or specific robots.txt directives for each crawler type.
Mistake 2: Allowing Everything Without Strategy
Why this happens: Default server configurations allow all crawlers. Teams assume "more crawlers = more visibility."
The problem: Training crawlers bulk-download your content, absorbing server resources and bandwidth without providing traffic in return. You're essentially subsidizing AI model training while competitors monetize training access.
How to fix it: Audit current crawler access. Implement 402 responses for training bots while maintaining user-facing access.
Prevention: Quarterly crawler audits to review which bots access your site and what value exchange exists.
Mistake 3: Ignoring Crawler Verification
Why this happens: Crawlers self-identify via user-agent strings, which can be spoofed. Teams trust user-agent headers without verification.
The problem: Malicious scrapers impersonate legitimate crawlers. You think you're allowing GPTBot but actually permitting unauthorized copying.
How to fix it: Use Cloudflare's verified bot detection or implement reverse DNS verification for major crawlers (OpenAI, Anthropic, Google publish their IP ranges).
Prevention: Enable Cloudflare Bot Management to distinguish verified crawlers from impersonators automatically.
Mistake 4: Setting and Forgetting Crawler Rules
Why this happens: Teams implement crawler rules once and never review them. New platforms launch with new crawlers that aren't addressed.
The problem: Your crawler strategy becomes outdated within months. New AI platforms (like Grok in 2024) can't access your content because rules predate their existence.
How to fix it: Set calendar reminders for quarterly crawler strategy reviews. Monitor Cloudflare dashboards for new crawler patterns.
Prevention: Subscribe to AI platform announcements. Major launches (new OpenAI features, Anthropic updates, Google AI changes) often introduce new crawlers.
Mistake 5: Not Communicating Licensing Terms Clearly
Why this happens: Teams block training crawlers with 403 Forbidden responses without explaining why or how to negotiate access.
The problem: AI companies receive a hard block with no path forward. You miss potential licensing revenue and relationship opportunities.
How to fix it: Use 402 Payment Required responses with clear contact information: "To license this content for AI training, email partnerships@yourcompany.com"
Prevention: Establish a content licensing contact and process before implementing 402 responses. Be prepared to negotiate when AI companies reach out.
> ✅ Ready to Optimize Your Crawler Strategy? Join 500+ e-commerce brands optimizing for AI visibility. Join the waitlist for AIVO's crawler management service →
FAQ: AI Crawler Management Questions Answered
1. Will blocking training bots like GPTBot hurt my search rankings?
No. Training bots (GPTBot, ClaudeBot, Google-Extended) are separate from search indexing bots. Blocking GPTBot doesn't affect ChatGPT's ability to cite you via ChatGPT-User. Blocking Google-Extended doesn't impact Google Search rankings at all. The bots serve different functions.
2. How do I know which crawlers are actually hitting my site?
Check your server logs for user agent strings, or use Cloudflare AI Crawl Control for a visual dashboard. Most hosting providers also offer basic bot traffic analytics. Look for patterns: training bots typically scrape in bulk, while user-facing bots show burst patterns aligned with actual query volume.
3. What's the difference between robots.txt blocking and Cloudflare blocking?
Robots.txt is a polite request; bots can ignore it (and some do). Cloudflare blocking happens at the edge before requests reach your server, making it impossible for bots to bypass. For compliance-conscious bots (OpenAI, Anthropic, Google), robots.txt works. For aggressive crawlers like Bytespider, use Cloudflare.
4. Can I allow some pages but charge for others?
Yes, with Cloudflare AI Crawl Control you can set different rules by path. Allow blog posts (you want citations) but charge for proprietary research reports. This granular control lets you balance visibility goals with content protection.
5. What happens when I send a 402 response to a training bot?
The bot receives an HTTP 402 status code with your custom message (typically contact information for licensing discussions). The bot can either respect the 402 and not crawl your content, or reach out to negotiate access. Over time, this creates a record of 402 responses that signals your content is valuable and protected.
6. Will using 402 responses hurt my AI platform visibility?
No, because you're only sending 402 to training bots, not user-facing crawlers. ChatGPT can still cite you via ChatGPT-User even if you block GPTBot with 402. Your visibility strategy and training data strategy are separate concerns.
7. How much can I actually charge with Cloudflare Pay Per Crawl?
Cloudflare Pay Per Crawl is in private beta with pricing models still being tested. Early implementations suggest per-request pricing in the $0.001-$0.01 range depending on content value. For high-traffic sites with premium content, this could generate significant revenue. The real value is establishing the norm that training data should be compensated.
8. Should news publishers manage AI crawlers differently than e-commerce sites?
Yes. News publishers depend heavily on AI platform citations for traffic, so being more permissive with user-facing crawlers makes sense. E-commerce sites with proprietary product data may want stricter controls on training bots to protect competitive advantage. Your content's strategic value determines your crawler strategy.
9. What if an AI company refuses to negotiate after I send 402 responses?
That's their choice, and it tells you something valuable: they don't value your content enough to pay for it, yet they want to use it anyway. In that case, escalate to a full 403 block. The point of 402 is to start conversations; if companies refuse to engage, blocking is justified.
10. How often should I review my AI crawler strategy?
Quarterly at minimum. New AI platforms launch constantly, crawler behavior changes, and business models evolve. What made sense in Q1 might be outdated by Q4. Set calendar reminders to review your Cloudflare AI Crawl Control dashboard and adjust rules based on actual traffic patterns and business outcomes.
Key Takeaways
Not all AI crawlers serve the same purpose.
User-facing bots like ChatGPT-User, Claude-Web, and Perplexity-User represent real user intent. They drive qualified traffic and should have unrestricted access. Training bots (GPTBot, ClaudeBot, Google-Extended) scrape content for model improvements without sending traffic back. Aggressive crawlers like Bytespider ignore standards and drain resources without providing value.
Strategic crawler management requires nuance, not blanket policies.
Allow user-facing crawlers to maximize AI platform visibility. Use 402 responses with training crawlers to signal your content has value and open licensing conversations. Block aggressive crawlers that ignore industry standards to protect your infrastructure. The "allow everything" or "block everything" approaches both leave money on the table.
Cloudflare AI Crawl Control makes implementation straightforward.
Visual dashboards show exactly which bots are accessing your site, traffic patterns over time, and granular controls for each crawler. Pay Per Crawl beta access enables actual content monetization instead of binary allow/block decisions. Implementation takes minutes, not hours.
The broken incentive model is being fixed, but action is required.
Over 1 billion HTTP 402 responses are sent daily as content creators demand fair compensation for training data. Cloudflare's Pay Per Crawl establishes infrastructure for automated licensing. Early adopters set industry norms and capture monetization opportunities that late entrants miss.
Your crawler strategy directly impacts AI visibility and revenue.
Block the wrong bots and you disappear from ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Claude citations. Allow everything and you give away valuable training data while absorbing server costs. Strategic decisions compound over time as AI platforms establish trusted source relationships. First-movers build authority that lasts.
For comprehensive AI visibility optimization beyond crawler configuration, explore our REVEAL Framework methodology or start with a free AI visibility audit.
What Does AI Crawler Management Mean for My Business?
Your AI crawler strategy directly impacts two critical business outcomes: visibility in AI platforms (where 40% of product discovery now happens) and protection of valuable content assets. User-facing crawlers (ChatGPT-User, Perplexity-User, Claude-Web) determine whether your brand appears in AI-generated responses when prospects search for solutions, with proper access driving 20-30% traffic increases within 90 days. Training crawlers (GPTBot, ClaudeBot, Google-Extended) currently take your content without compensation, making your original research and proprietary insights into training data for models that compete with your business. The window for establishing good crawler relationships is now while AI platforms are learning which sources to trust and which publishers respect their terms. Strategic differentiation by crawler type positions you for both visibility opportunity and content monetization.
If you manage significant content assets in 2025, your AI crawler strategy directly impacts two critical business outcomes: visibility in AI platforms and protection of valuable content.
For visibility: User-facing crawlers (ChatGPT-User, Perplexity-User, Claude-Web) determine whether your brand appears in AI-generated responses. These platforms now drive 40% of product discovery. Block these crawlers and you effectively opt out of the fastest-growing search channel. Allow them strategically and you build citation history that compounds as AI platforms learn which sources to trust.
For content protection: Training crawlers (GPTBot, ClaudeBot, Google-Extended) currently take your content without compensation. Your original research, detailed guides, and proprietary insights become training data for models that compete with your business. The 402 response framework and Pay Per Crawl beta access finally give content creators leverage to negotiate fair value exchange.
The window for establishing good crawler relationships is now. AI platforms are still learning which sources to trust, which publishers respect their terms, and which content provides consistently high quality. Early decisions create precedents. Sites that block everything miss the visibility opportunity. Sites that allow everything miss the monetization opportunity. Strategic differentiation by crawler type positions you optimally for both.
Next Steps
Immediate Action (This Week)
Step 1: Audit Current Crawler Access
- Check your server logs or Cloudflare dashboard to see which AI crawlers are currently accessing your site
- Identify which user-facing crawlers (ChatGPT-User, Claude-Web, Perplexity-User) you're allowing or accidentally blocking
- Review your robots.txt file for overly broad AI bot blocks that might be hurting visibility
> ⚡ Quick Start: Use AIVO's free robots.txt checker to instantly see which AI crawlers can access your content
Short-Term Action (This Month)
Step 2: Implement Strategic Crawler Rules
- Set up Cloudflare AI Crawl Control if you haven't already (free tier available)
- Configure allow rules for user-facing crawlers (ChatGPT-User, Perplexity-User, Claude-Web, OAI-SearchBot)
- Implement 402 responses for training bots (GPTBot, ClaudeBot, Google-Extended) with licensing contact information
- Block aggressive crawlers (Bytespider, unverified scrapers)
Step 3: Monitor Impact
- Track AI platform citations through manual sampling (search relevant queries on ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude)
- Monitor referral traffic from AI platforms in Google Analytics 4
- Review Cloudflare dashboards weekly for crawler traffic patterns
- Document which crawlers drive actual traffic vs. just consuming bandwidth
Long-Term Action (This Quarter)
Step 4: Optimize and Monetize
- Apply for Cloudflare Pay Per Crawl private beta if your site has premium content worth licensing
- Develop a content licensing strategy for training data monetization opportunities
- Establish quarterly reviews of crawler strategy as AI landscape evolves rapidly
- Build relationships with AI platforms for priority crawling or partnership opportunities
Step 5: Stay Current
- Subscribe to AI platform announcements (OpenAI, Anthropic, Google AI, X AI)
- Set calendar reminders for quarterly crawler strategy reviews
- Join AIVO's newsletter for crawler management updates and industry changes
- Test new crawler configurations as platforms evolve
> 🚀 Ready to Optimize Your AI Visibility? > > AIVO helps mid-market companies navigate AI visibility optimization with systematic, measurable strategies. From crawler management to citation optimization, we ensure your content works as hard in AI platforms as it does in traditional search. > > What you get: > - Comprehensive crawler audit across all major AI platforms > - Strategic access control implementation with Cloudflare > - Pay Per Crawl beta application assistance > - Quarterly strategy reviews as landscape evolves > - Priority support for urgent crawler issues > > Schedule a free crawler strategy consultation →
Related Resources
AIVO Tools:
- Free Robots.txt Checker - Analyze which AI crawlers can access your site
- AI Visibility Audit - Comprehensive assessment of your AI platform presence
- AI Visibility Tools Directory - Complete toolkit for AI optimization
- ChatGPT SEO Optimization Guide 2025 - Optimize content for ChatGPT citations
- AI Visibility Tools Directory Strategic Guide - Leverage free tools for competitive advantage
- The REVEAL Framework - AIVO's comprehensive AI visibility methodology
- Cloudflare AI Crawl Control Documentation - Official implementation guide
- OpenAI GPTBot Documentation - GPTBot specifications and control methods
- Anthropic Claude Bot Documentation - ClaudeBot access control
About This Guide
Last updated: November 9, 2025 Content maintained by: AI Visibility Agency Questions or feedback? Contact our team